In modern photonics and precision optical applications, Half Ball Lens play a critical role in light coupling, beam shaping, and fiber-optic communications. As a specialized optical component, they offer unique advantages in collimating and focusing laser beams while maintaining compact form factors. Hypoptics, a leading optical components manufacturer, provides precision-engineered Half Ball Lens for demanding applications across industries.
A half ball lens is precisely what its name suggests—a spherical lens that has been cut in half, creating a flat surface while maintaining the curved dome on the opposite side. This design enables efficient light manipulation, where the spherical surface refracts incoming light while the flat surface allows for easy mounting and alignment. Common materials include fused silica, BK7, and sapphire, each offering distinct advantages in refractive index, durability, and thermal stability.

Different applications call for different optical geometries. Full ball lenses provide symmetrical focusing across all angles, making them ideal for imaging and omnidirectional light collection. In contrast, Half Ball Lens offer more controlled light interaction, making them better suited for fiber-optic coupling, laser diode collimation, and applications where precise beam directionality is required. The flat surface also simplifies integration into optical systems by enabling stable mounting without additional supports.
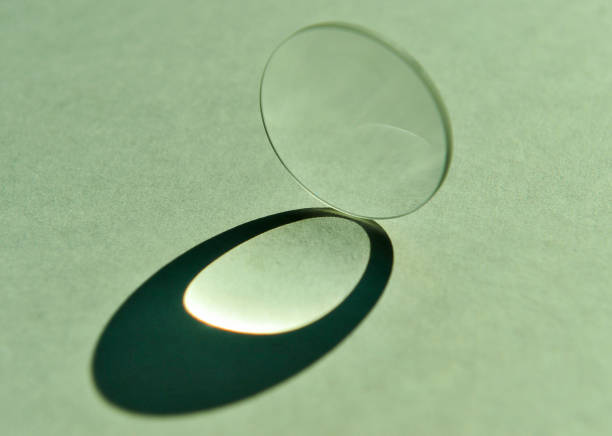
The unique optical properties of Half Ball Lens make them indispensable in multiple fields. Fiber-optic telecommunications rely on them for efficient light coupling between fibers and laser sources. Medical devices, including endoscopes and surgical lasers, utilize them to focus and redirect light in compact spaces. Laser scanning and barcode readers integrate Half Ball Lens to enhance beam shaping, while in scientific instrumentation, they assist in fluorescence microscopy and spectroscopy setups.
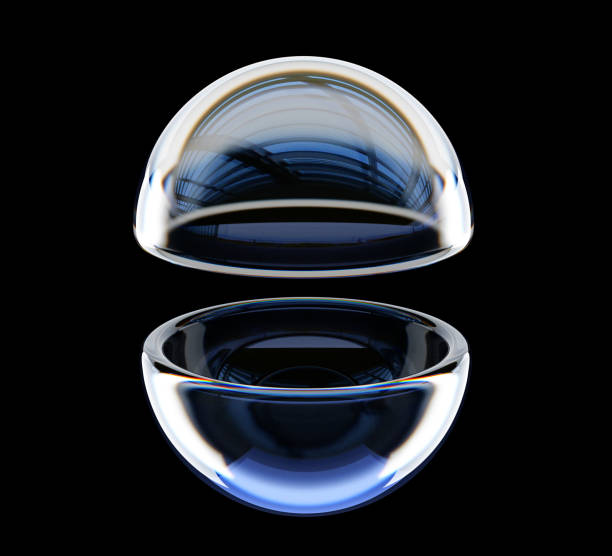

Achieving optimal performance with Half Ball Lens requires careful optical alignment. The flat surface should face the light source or detector, while the curved surface interacts with the incoming or outgoing beam. Positioning them at the correct working distance ensures minimal spherical aberration. Using anti-reflective (AR) coatings—available on select Hypoptics lenses—helps maximize light transmission, particularly in high-power laser applications. Secure mounting with low-stress adhesives preserves alignment while preventing mechanical degradation over time.

When choosing a half ball lens, key factors to evaluate include material selection (thermal expansion, durability, and refractive index), diameter and radius of curvature (affecting focal length and beam shaping capability), and surface quality (scratch-dig specifications for minimal scattering). The operating wavelength range (UV, visible, or IR) determines whether standard or specialty coatings are needed. Hypoptics offers options with AR coatings, high-precision polishing, and custom sizing to meet exact application requirements.
From laser beam shaping to fiber-optic coupling, Half Ball Lens offer a versatile and efficient solution for optical system designers. With their compact form, simplified mounting, and beam control advantages, they overcome many limitations of traditional lenses. Hypoptics’ high-quality Half Ball Lens ensure reliability across medical, industrial, and scientific applications, delivering precision-engineered performance with minimal optical loss.
 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email us:
Email us:  9B-4F, No.1 Qingnian Road Liando U Valley,Yuhua International Wisdom Valley, Nanjing, 210039 China
9B-4F, No.1 Qingnian Road Liando U Valley,Yuhua International Wisdom Valley, Nanjing, 210039 China 








 English
English  cn
cn  de
de  es
es  fr
fr 


